Understanding ISO
1. What is ISO?
- ISO stands for International Standards Organization. ISO controls your camera sensor's sensitivity to light. Lower ISO (e.g., 100) is for bright scenes; higher ISO (e.g., 800+) is for low light.
2. ISO and Exposure:
- Low ISO keeps images clean and sharp, ideal for daylight. High ISO brightens dark scenes but can introduce grainy "noise."
3. When to Use Different ISO Levels:
- Daylight: Use low ISO (100–200) for best quality.
- Indoors/Low Light: Increase ISO (800+) for clearer shots without blur.
- Night Photography: High ISO (1600+) helps capture details in very low light.
4. ISO, Shutter Speed, and Aperture:
- Adjust ISO along with shutter speed and aperture to control exposure and capture motion.
5. Quick Tips:
- Start with low ISO and increase only as needed.
- Use Auto ISO for easy adjustments in changing light.
- Experiment to find the ISO range that works best for your camera and style.
Experimenting with ISO helps you find the balance between light sensitivity and image quality for any scene.

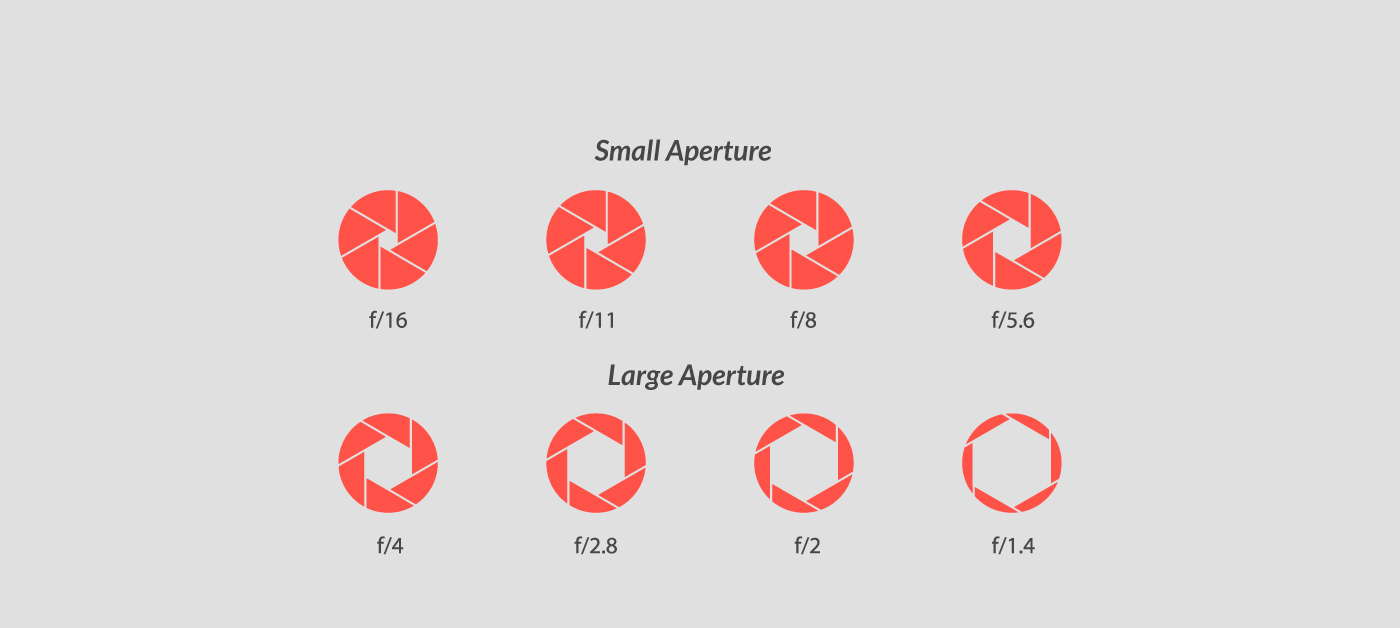
Adjusting Aperture
Aperture controls how much light enters your camera and affects focus depth. Lower f-stops (e.g., f/1.8) mean a wide aperture that brightens photos and blurs backgrounds—great for portraits. Higher f-stops (e.g., f/16) narrow the aperture, keeping more of the image in focus, ideal for landscapes. In low light, a wide aperture lets you capture more light without raising ISO. Adjusting aperture helps control exposure and focus depth, giving you creative control over each shot.
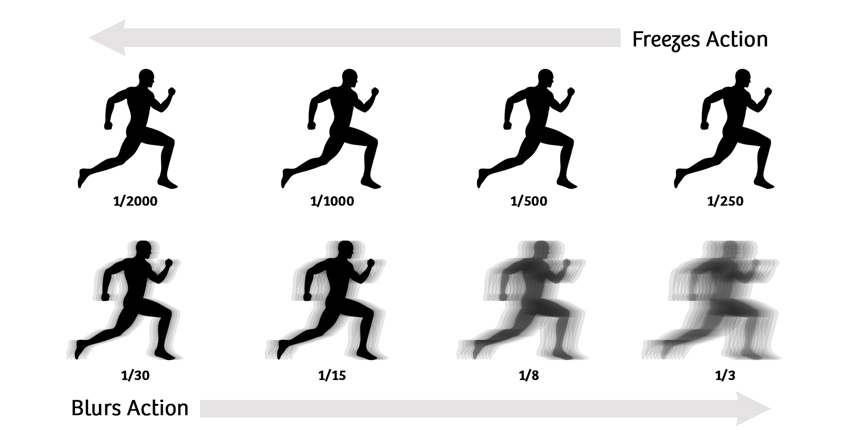
Shutter Speed
Shutter speed affects how long your camera sensor is exposed to light. Fast shutter speeds (e.g., 1/1000s) freeze motion, while slower speeds (e.g., 1/30s) create a motion blur effect. Experiment with both to add dynamics to your photos!
White Balance
White balance adjusts the color temperature of your images. Using the correct white balance setting helps avoid unnatural color tints. Try experimenting with daylight, tungsten, and fluorescent settings to achieve the desired mood in your shots.

Camera Modes
Most cameras have different modes, including Auto, Aperture Priority, Shutter Priority, and Manual. Understanding when to use each mode is crucial for getting the best results in various situations.
